- en Change Region
- Global Site
Application Notes
3D image analysis reveals drug-induced cellular senescence and increased nucleolus volume: Efficient imaging methods to maximize data acquisition
November 2024
High content analysis incorporates multiple measurements such as cell morphology and fluorescence intensity of specifically-labelled cellular features to assess biological activity in response to set of conditions, and is a powerful approach for applications like drug compound screening. Wide-field microscopy offers relatively high imaging throughput, which is ideal for screening drug candidate compounds, while confocal laser scanning microscopy enables three-dimensional visualization of structures and volumetric quantification to obtain deeper insight into compound responses. Using both wide-field and confocal laser scanning microscopy, drug discovery and life science research can be advanced more efficiently. In this application note, we introduce an imaging method that efficiently utilizes both 2D and 3D analysis of wide-field and confocal images to reveal how drug-induced cellular senescence impacts the nucleolus.
Keywords: cellular senescence, high content analysis, wide-field microscopy, confocal microscopy, 3D analysis, volume measurement, nucleolus, DNA damage, γH2AX, granule analysis, drug discovery
Sample preparation and experimental results
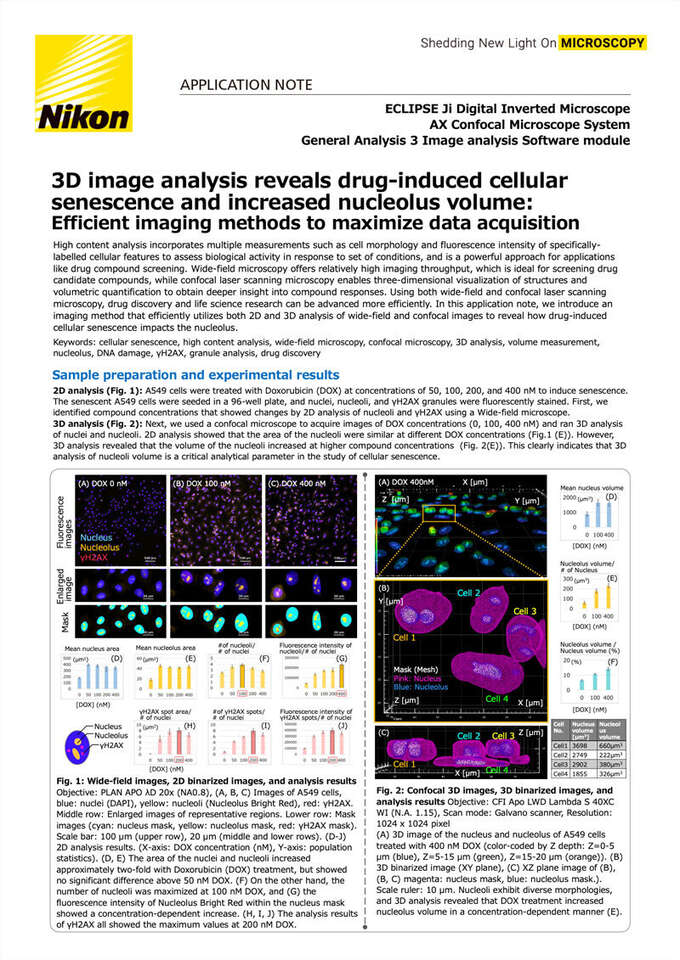
2D analysis (Fig. 1): A549 cells were treated with Doxorubicin (DOX) at concentrations of 50, 100, 200, and 400 nM to induce senescence. The senescent A549 cells were seeded in a 96-well plate, and nuclei, nucleoli, and γH2AX granules were fluorescently stained. First, we identified compound concentrations that showed changes by 2D analysis of nucleoli and γH2AX using a Wide-field microscope.
3D analysis (Fig. 2): Next, we used a confocal microscope to acquire images of DOX concentrations (0, 100, 400 nM) and ran 3D analysis of nuclei and nucleoli. 2D analysis showed that the area of the nucleoli were similar at different DOX concentrations (Fig.1 (E)). However, 3D analysis revealed that the volume of the nucleoli increased at higher compound concentrations (Fig. 2(E)). This clearly indicates that 3D analysis of nucleoli volume is a critical analytical parameter in the study of cellular senescence.
Fig. 1: Wide-field images, 2D binarized images, and analysis results Objective: PLAN APO λD 20x (NA0.8), (A, B, C) Images of A549 cells, blue: nuclei (DAPI), yellow: nucleoli (Nucleolus Bright Red), red: γH2AX. Middle row: Enlarged images of representative regions. Lower row: Mask images (cyan: nucleus mask, yellow: nucleolus mask, red: γH2AX mask). Scale bar: 100 µm (upper row), 20 µm (middle and lower rows). (D-J) 2D analysis results. (X-axis: DOX concentration (nM), Y-axis: population statistics). (D, E) The area of the nuclei and nucleoli increased approximately two-fold with Doxorubicin (DOX) treatment, but showed no significant difference above 50 nM DOX. (F) On the other hand, the number of nucleoli was maximized at 100 nM DOX, and (G) the fluorescence intensity of Nucleolus Bright Red within the nucleus mask showed a concentration-dependent increase. (H, I, J) The analysis results of γH2AX all showed the maximum values at 200 nM DOX.
Fig. 2: Confocal 3D images, 3D binarized images, and analysis results Objective: CFI Apo LWD Lambda S 40XC WI (N.A. 1.15), Scan mode: Galvano scanner, Resolution: 1024 x 1024 pixel
(A) 3D image of the nucleus and nucleolus of A549 cells treated with 400 nM DOX (color-coded by Z depth: Z=0-5 μm (blue), Z=5-15 μm (green), Z=15-20 μm (orange)). (B) 3D binarized image (XY plane), (C) XZ plane image of (B), (B, C) magenta: nucleus mask, blue: nucleolus mask.). Scale ruler: 10 μm. Nucleoli exhibit diverse morphologies, and 3D analysis revealed that DOX treatment increased nucleolus volume in a concentration-dependent manner (E).
Fast imaging with a large field of view and high resolution to capture tiny granules of γH2AX
ECLIPSE Ji built-in camera and 20x Lambda D objective combine to achieve a resolution per pixel of 0.316 μm/pixel.
Even small granular structures of less than 1 μm in size can be resolved with a low-magnification 20x objective, allowing the capture of a large number of cells in a single shot with the potential for quantitative statistical analysis.
2D & 3D high-content analysis to maximize data acquisition efficiency
Table. 2: Detection area, fluorescent labels, and conditions for image acquisition using a wide-field microscope for Fig 1.
Table. 3: Detection area, fluorescent labels, and conditions for image acquisition using a confocal laser-scanning microscope for Fig 2.
Fast, accurate imaging for new discoveries
In this experiment, we used a wide-field microscope to capture a large number of images in a short time, allowing us to study the effects of a drug on variably-treated populations across the entire plate. A single, fully in-focus EDF image was constructed from three Z-stack images, and the nuclei, nucleoli, and γH2AX granules were binarized and measured.γH2AX granules appeared with maximum count, area, and fluorescence intensity at 200 nM DOX treatment. On the other hand, the number of nucleoli and their fluorescence intensities were maximal with 100 and 400 nM Dox treatment, respectively. The area of nucleoli showed no difference with drug concentration above 50 nM. To then study subcellular details, confocal images of A549 cells at three different drug concentrations were acquired. The 3D confocal images were binarized and the volumes of the nuclei and nucleoli were measured. The results of the 3D analysis revealed that high concentrations of Doxorubicin increased nucleolus volume.
Sample Preparation Protocol
Please refer to the Nikon ECLIPSE Ji Application Note for the A549 cell senescence induction and sample preparation protocol ”Label-free quantitative analysis of cellular senescence and high-content imaging of granules”
Cell staining protocol
DNA Damage Detection Kit - γH2AX - Deep Red
*This is slightly different from the method described in the G267 instruction manual.
- Remove the cell culture supernatant, add 4% PFA solution (100 μl/well) to each well, and incubate at room temperature for 3 minutes.
- Remove the PFA solution and wash the cells three times with PBS (100 μl/well).
- add 0.1% Triton X-100/PBS solution (100 μl/well) and incubate at room temperature for 30 minutes.
- Remove the supernatant and wash the cells twice with PBS (100 μl/well).
- Add Blocking Solution (100 μl/well) and incubate for 20 minutes at room temperature.
- Remove the supernatant and wash the cells twice with PBS (100 μl/well).
- Add γH2AX staining solution (100 μl/well) and incubate overnight at 4 degrees.
- Remove the supernatant and wash the cells twice with PBS (100 μl/well).
- Add Secondary antibody staining solution (100μl/well) and incubate for 1 hour at room temperature.1
- Remove the supernatant and wash the cells twice with PBS (100 μl/well).
Nucleolus Bright Red
- After γH2AX staining, remove the supernatant and add a mixture of adjusted Nucleolus Bright working solution and DAPI (100 μl/well) and incubate at room temperature for 5 minutes. *Please refer to the instruction manual of N512. Nucleolus Bright Red:1000x dilution, DAPI:1000x dilution https://www.dojindo.co.jp/manual/N511_N512/
- The supernatant is removed and the cells are washed twice with PBS (100 μl/well).
Summary
✔︎ Fast, 2D statistical analysis with wide-field microscopy
✔︎ Three-dimensional structural examination and 3D analysis with confocal laser scanning microscopy
✔︎ Volumetric information leads to new discoveries
✔︎ Efficient imaging was combined 2D and 3D analysis
✔︎ Nucleolus volume is a useful analytical parameter in the study of cellular senescence
✔︎ Combined imaging modalities allow accurate detection of drug effects
✔︎ Seamless 2D & 3D analysis from drug discovery to pharmacological effects with a single ECLIPSE Ji
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our sincere gratitude to everyone at Dojindo Laboratories for their cooperation in establishing the experimental conditions for senescence induction and the staining conditions protocol optimized for imaging.
References
Abigail Buchwalter, et al., Nucleolar expansion and elevated protein translation in premature aging. Nature Communications volume 8, Article number: 328 (2017)
Alba Corman, et al., Targeting the nucleolus as a therapeutic strategy in human disease. Trends Biochem Sci. Volume 48, Issue 3, March 2023, Pages 274-287
Product information
ECLIPSE Ji Digital Inverted Microscope with AX Confocal Microscope System
The ECLIPSE Ji is capable of fast, high-resolution image acquisition using its built-in camera and epi-fluorescence light source. This digital inverted microscope is optimized for 2D high content analysis, with the ability to upgrade to confocal when required. From drug screening using fast wide-field imaging to understanding three-dimensional structures and 3D analysis using confocal images, you can obtain seamless results with this single unit.
General Analysis 3 image analysis software module
By simply combining analysis blocks, nucleus and nucleolus regions can be easily binarized and measured, allowing flexible image analysis.
The ”ConnectCells 3D” function allows you to easily perform 3D analysis in steps similar to a 2D analysis.
