- en Change Region
- Global Site
- Home
- CRO
- Europe
- Applications
- Histological Image Segmentation

Nikon BioImaging Labratories
Europe
Histological Image Segmentation
Histological image analysis is a crucial aspect of medical research and diagnostics. It involves the microscopic examination of tissue samples that have been stained to highlight different cellular components and structures. This analysis allows pathologists to diagnose diseases, understand cellular interactions, and conduct detailed anatomical studies. The accuracy of histological analysis is vital, as it directly impacts clinical decisions and the understanding of complex biological processes.
Challenges
The intricacies of histological image segmentation stem from the way these images are typically obtained. In histology, the stains and dyes applied to tissue samples are absorptive rather than fluorescent. They are visualized in full color under white light illumination, and unlike in fluorescence microscopy, the data from various stains are not distinctly separated based on light emission. Thresholding, a simple segmentation method that separates objects based on pixel intensity, often falls short due to the variability in stain absorption and the complex morphology of tissues, including the presence of various cell types with diverse shapes and sizes. Consequently, the segmentation and analysis of histological images have traditionally relied heavily on manual inspection by experienced professionals, a process that is both time-consuming and subjective.
Solutions
Artificial intelligence (AI) offers a solution for the precise and efficient segmentation of histological images. Deep learning-based algorithms can segment images of complex tissue samples with human-like accuracy, learning from annotated examples to identify numerous features swiftly. Once trained, AI can quickly discern thousands of elements in images, streamlining pre-clinical research by reducing manual effort and enhancing the discovery of disease pathways and treatment options.
Method
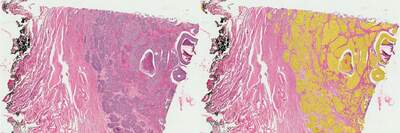
In our study, we utilized AI to enhance the analysis of histological slides, focusing on a human cervical cancer specimen stained with the conventional Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) method. This staining technique is intentionally nonspecific—hematoxylin colors nuclei blue and eosin imparts a pink hue to the cytoplasm, thus providing a stark contrast that facilitates the examination of the entire tissue section. Despite its simplicity, the H&E method introduces challenges in segmentation, as it requires careful consideration of the brightness of the stain and the diverse sizes and shapes of cellular structures.
To address these challenges, we developed multiple AI networks, each tailored to identify and differentiate features across varying scales, from large tumor masses down to red blood cells and single cell nuclei. These networks underwent a training process using a small, annotated segment of the histological image and were subsequently deployed to analyze the full extent of the tissue sample.
Results
Our analysis revealed that the tumor regions accounted for approximately 21% of the total tissue area examined. The AI-driven segmentation process successfully delineated around 360,000 nuclei, with 132,000 of those located within the tumor areas.
Conclusion
The application of the trained neural networks allowed for the rapid processing of an extensive 9.5 x 7 mm image in a matter of seconds. These results are promising for future studies, as the networks could be adapted for analyzing other H&E-stained tissues, either in their current form or with minor modifications to accommodate different sample characteristics, thus significantly accelerating the pre-clinical research workflow.
Contact
- Home
- CRO
- Europe
- Applications
- Histological Image Segmentation
